Blog Archives
‘Hamlet,’ Kenny Leon’s Dynamite Version, Free Shakespeare in the Park

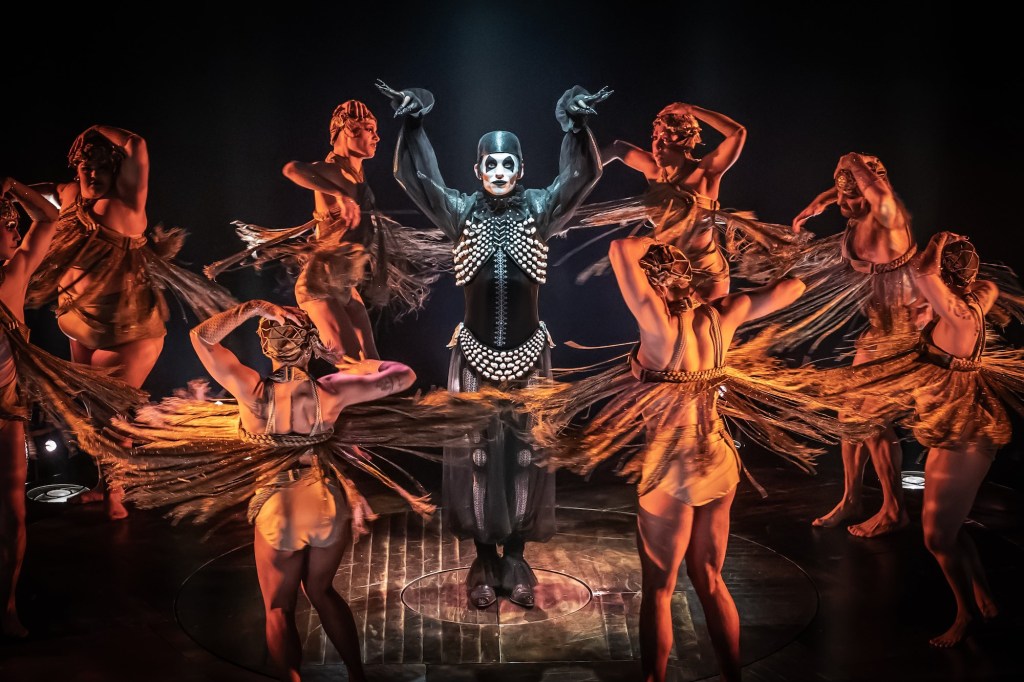
There are more iterations of Hamlet presented globally in the last fifty years than are “dreamt of in your philosophy.” To that point director Kenny Leon’s version of Hamlet, currently at the Delacorte Theater in Central Park until August 6th, provides an intriguing update of the son for whom time is so “out of joint,” he is unable to seamlessly and speedily avenge his father’s murder. Leon’s version shapes a familial revenge tragedy. Once set on its course, dire events cannot be averted, for at the core is the initial corruption, “the primal eldest curse, a brother’s murder” that “smells to heaven.” From that there is no turning, until justice is served, the sooner the better.
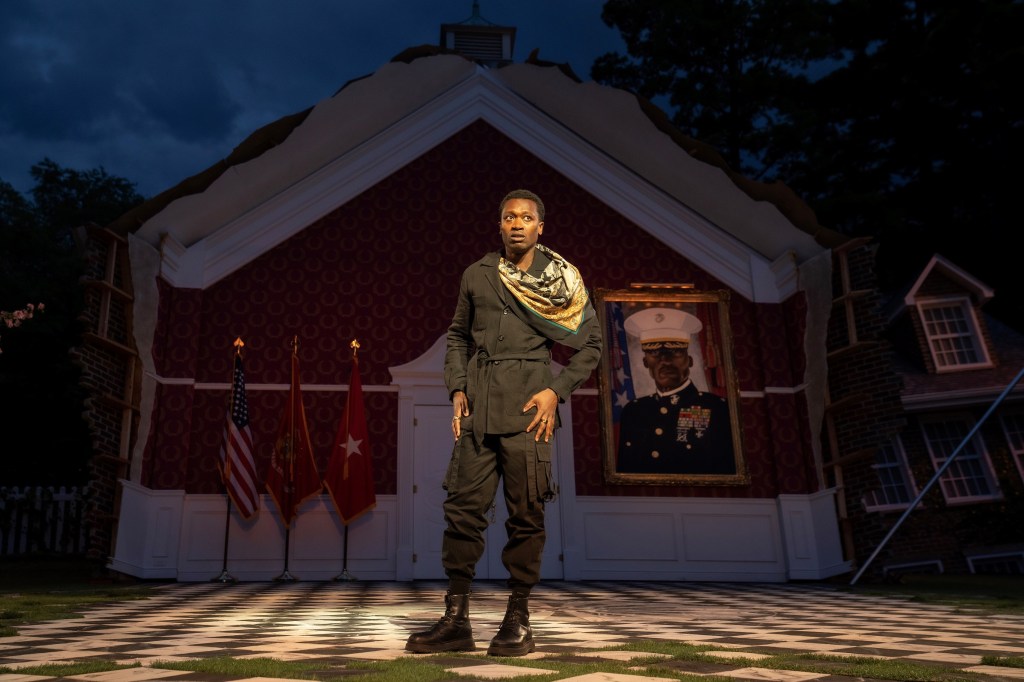
In this 61st offering of Free Shakespeare in the Park, we immediately note the conceit of corruption and its ill effects to skew the right order of things, making them “out of joint,” off-kilter. This is an important theme of the play (expressed by Hamlet) and represented by Beowulf Boritt’s set, some of which is a wrecked-out remnant of his design from Leon’s pre-Covid production of Shakespeare’s comedy, Much Ado About Nothing.

That 2019 design sported a resplendent, brick, Georgian mansion that stylistically conveyed the wealth and rectitude of its Black, lordly owners rising up in a progressive South. Hope was represented by a “Stacy Abrams for President” campaign sign proudly displayed on the side of the building. A towering flagpole and American flag patriotically stood like a sentinel at the ready. Peace and order reigned.
It is not necessary to have seen Much Ado About Nothing to understand the ruination and disorder foreshadowed by Boritt’s Hamlet set which coherently synthesizes Leon’s themes for his modernized version. In one section a tilted smaller version of the former Georgian house appears to be sinking off its foundation. On stage left, an SUV is tilted off center, undrivable, in a ditch. The Stacy Abrams’ sign is torn and displaced on the ground like discarded trash. And the American flag with its long flagpole angled toward the ground signals distress and a “cry for help.”

The only ordered structure is the cutaway of a building center stage (used for projections), whose door the characters enter and exit from.
Boritt’s set design suggests “something is rotten” unstable and “out of joint” in this kingdom. Themes of devolution are foreshadowed. From unrectified corruption comes disorder which breeds chaos and dark energy, out of which destruction and death follow. And all of this springs from the unjust murder of the deceased in the coffin that is draped in an American flag and placed center stage. It is his life which is celebrated by the beautiful singing of praise hymns at his well-attended funeral in the prologue of Leon’s Hamlet. It is his life that is memorialized by the huge portrait of the kingly father in military dress which hangs watchful, presiding over events from its position on the back wall of the only part of the set that is not wrecked and disarrayed.

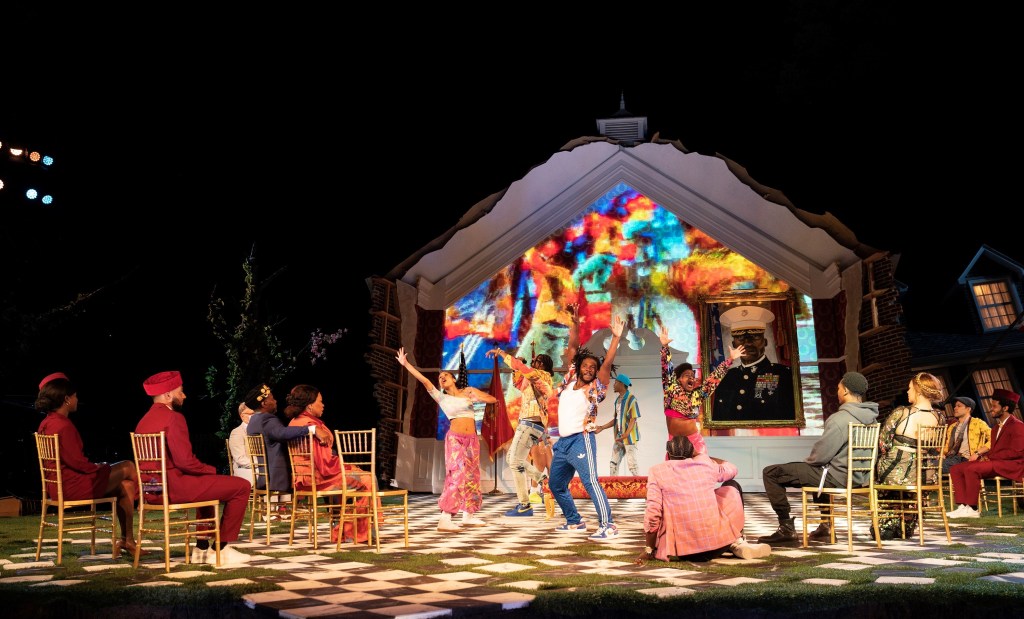
Cutting Act I scene i (soldiers stand on guard watchful of an attack from Norway), Leon opens with the elder Hamlet’s funeral. A Praise Team joined by a Wedding Singer, who we later recognize to be Ophelia (the golden-voiced Solea Pfeiffer), sing with beautiful harmony. Jason Michael Webb created the music and additional lyrics which set out the Godly tenets that all are importuned to follow or live by. To their downfall they don’t and this is manifested in tragedy.
Importantly, the first three songs are taken from the Bible. The first is from Ecclesiastes (“To everything there is a season). Then follow Matthew 5 (“To show the world your love, I’m goona let it shine”) and I John 5 (“When you go on that journey you go alone”). The last song that Ophelia sings is composed of lines from a love poem that Hamlet wrote for her.
The songs intimate the former moral rectitude and divine unctions found in the former Hamlet’s kingdom. Ironically, the memorial service represents the last peace that this kingdom will appreciate. As the set indicates, wrack and ruin have already begun. The scenes after the funeral represent declension and growing darkness. And after old Hamlet is buried, nothing good follows.

Numerous cuts (scenes, lines, characters) abound in Leon’s version. His iteration presents questions about the disastrous consequences of familial revenge which is different from Godly justice suggested by the songs. Importantly, Leon’s update (sans scene i) gets to the crux of the conflict with scene ii, the marriage celebration of Claudius (the terrific John Douglas Thompson and Gertrude (Lorraine Toussaint is every inch Thompson’s equal). We note their public affection for one another, which Hamlet later intimates is a lust-filled marriage in an “unseemly bed.” The partying has followed fast upon the old Hamlet’s burial, to the dismay and depression of his loyal son.
It is during the festivities when the sinister intent of the new king and duped mother Gertrude chide Hamlet (the fabulous Ato Blankson-Wood). They suggest he put off his mourning clothes, “unmanly grief” and depression for it is “unnatural.” Already, the cover-up has begun and Hamlet is the one individual Claudius must be circumspect about as the rightful heir to a throne which he usurped.
Gertrude importunes Hamlet to remain in the kingdom instead of returning to his studies in Wittenberg, and dutifully, he obeys, stuck with the daily reminder of his father’s death and mother’s “o’er hasty marriage.” This version emphasizes Claudius’ sincerity covering over his suspicion and fear of Hamlet. He is happy to keep him under his watchful eye. Throughout his magnificent portrayal, Thompson’s Claudius gradually reveals his underlying guilt and fear for his crimes of regicide and fratricide. We see his behavior grow more and more paranoid about Hamlet as the conflict between them grows and Hamlet unloads snide remarks on Claudius, Polonius and all those who are obedient to the usurper king as a provocation.

Leon’s version is a familial revenge tragedy which eliminates any reference to Norway or Prince Fortinbras seeking justice for his father’s death in battle with Denmark. Leon is unconcerned with Norway and Fortinbras. The conflict in his Hamlet is internal to Denmark, a divided kingdom like “an unweeded garden, rank and gross in nature.” Divided against itself, with brother vs. brother and son vs. uncle, and Gertrude the exploited, seduced pawn, Claudius’ guilt is a canker worm which gnaws at him. Likewise, gnawing at Hamlet after his father’s ghost’s visit, is the knowledge of what has to be done. But he maintains, “cursed spite, that ever I was born to set it right.”
All is covert and the truth is covered up. Polonius and Claudius spy on Hamlet to divine why he is “mad,” and Hamlet acts mad and rejects Ophelia’s love during the process of divining whether the ghost is telling the truth. Intrigue, chaos and darkness augment and have their way with the innocent and guilty. For Hamlet, the “time is out of joint.” An intellect, he is “blunted” (the ghost later says) from making the correct decisions or acting upon them in a timely fashion. The darkness that Claudius has set loose taints Hamlet and every principal character that must show obeisance to King Claudius’ illegal reign.

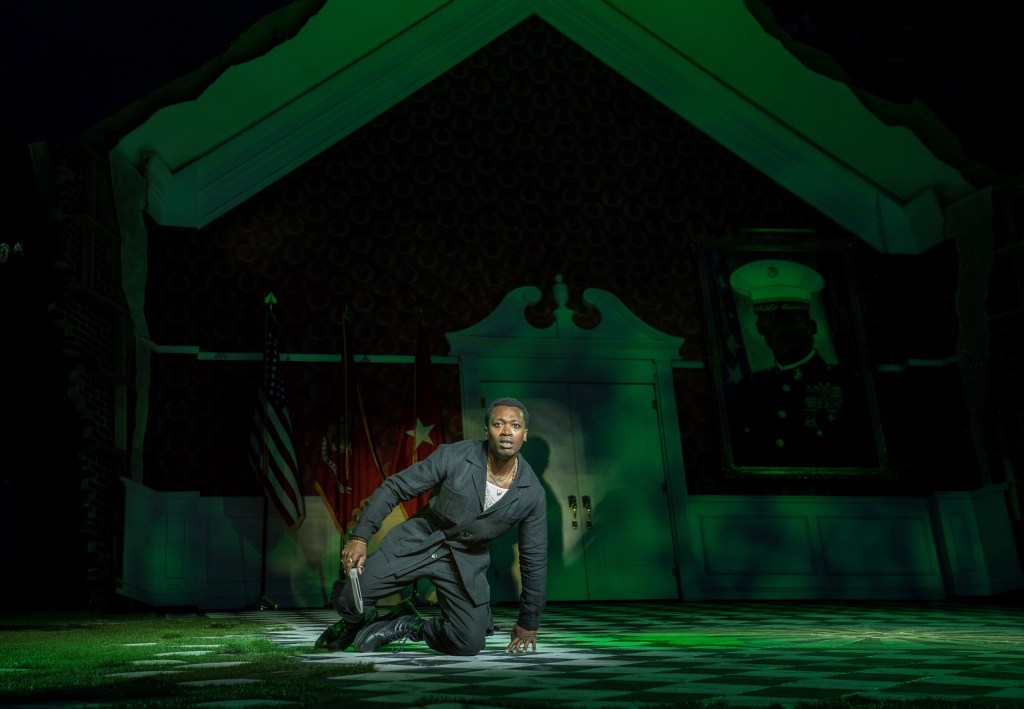
Key to the argument of choosing vengeance vs. justice is the enthralling scene when Hamlet meets his father’s ghost. Initially, the creative team (Jeff Sugg’s projections, Allen Lee Hughes’ lighting design, Justin Ellington’s sound design) present the father’s ghost on the back wall with projections on the portrait and the wall, accompanied by the ghost’s booming, shattering voice, which commands Hamlet’s obedience.
But at the description of the murder, the ghost possesses Hamlet. Blankson-Wood’s performance of the ghost consuming his soul is phenomenal and physical. He arches his back with the jolt of spirit possession and then rights his gyrating body as his father’s voice spews wildly from him, eyes rolled back, arms waving, the very picture of the demonic that Horatio (the fine Warner Miller) warned Hamlet might “tempt him to the flood.” At once frightening and mesmerizing, the possession enthralls us and changes Hamlet. It is a dynamic, successful scene showing the decline in the goodness from the initial praise songs to the devolution of the spirit’s will demanding vengeance. We are thunderstruck. Blankson-Wood’s authenticity frightfully convinces us of the spirit’s potential for evil misdirection into a vengeance which is not just and will bring devastation.
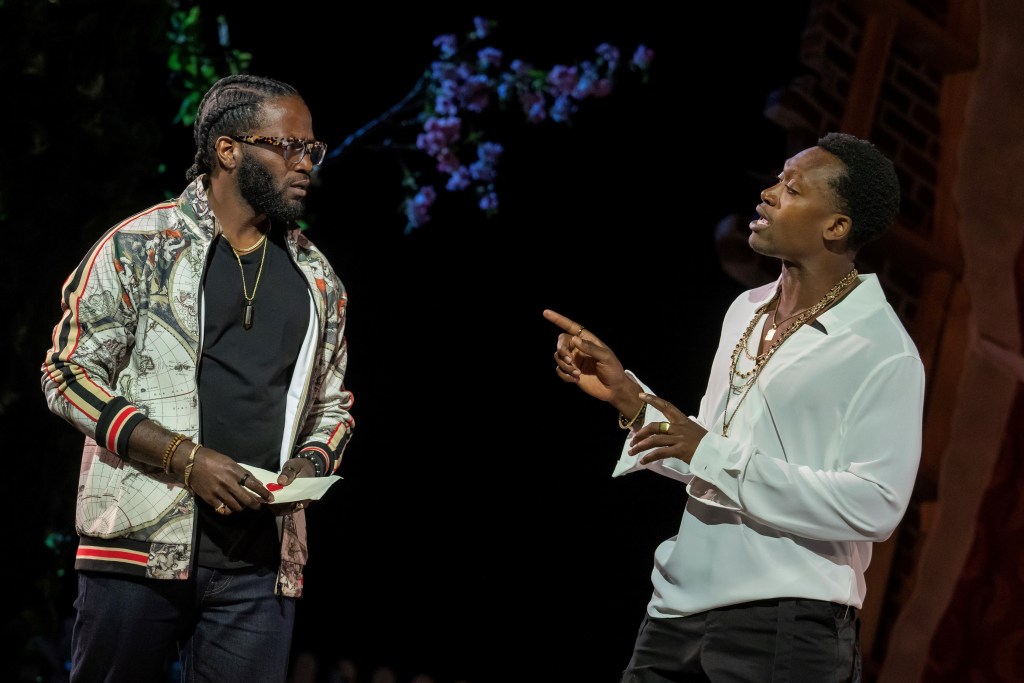

After the ghost leaves the vessel it inhabited and Hamlet swears Horatio and Marcellus (Lance Alexander Smith) to secrecy, Hamlet’s fate is sealed. He moves toward faith in the ghost, farther away from the light-filled unctions in the songs at his father’s funeral. Now, there is no “showing love” and “shining one’s light.” Intrigue and acting “mad” and conspiracy and cover-up overtake the mission of the kingdom. Hamlet toys with and ridicules Polonius (Daniel Pearce gives a humorous, organically funny portrayal) and does the same with Ophelia in a powerful scene, eschewing his love for her. Pfeiffer’s Ophelia shows her devastation and shock. His behavior is a complicating truth for everyone and it intensifies Hamlet’s conflict with Claudius.
Knowing Hamlet’s madness is not for Ophelia’s love, Claudius grows more paranoid and guilt laden. Clearly, when the actors make their presentation of the dumb show (Jason Michael Webb’s song “Cold World” is superb), and Hamlet presents ‘The Murder of Gonzago,’ he and Horatio see that Claudius’ guilty conscience is made manifest in ire and defensiveness. Though this scene is truncated, as is Hamlet’s description of how the actors should proclaim their speeches, no coherence is lost. Claudius runs away, his soul uncovered. Hamlet is convinced vengeance is the right course of action. But he has allowed himself to be misguided. Nothing good will come of following the ghost’s lead.

Leon truncates the minor speeches, retaining those that convey Hamlet’s angst at being stuck in the kingdom which is a prison. He can’t commit suicide (“To Be or Not to Be”) because his morality and fear of death forbids it. Stuck in Denmark, everyone is a potential enemy except Horatio. He uses coded speech with everyone especially Rosencrantz and Guildenstern, who Claudius/Gertrude have engaged to spy on him. Ato Blankson-Wood delivers the key soliloquies powerfully with insight as he makes the audience his empathetic confidante who understands his intellect has chained him to inaction. We are drawn into his plight, but become frustrated when his determination falters.
The paramount event where his intellect intrudes happens when Claudius is praying in the church (fine stylized staging). Coming upon Claudius, Hamlet rejects the opportunity to kill him because he thinks Claudius is confessing his sins and getting right with God. However, it is a missed opportunity which Hamlet squanders because Claudius’ prayers fail (“my words fly up, my thoughts remain below; words without thoughts never to heaven go.”). Claudius realizes to receive forgiveness he would have to give up the throne, Queen and his cover-up which he will never do.
Hamlet lacks proper discernment and moves from his bad decision to impulse. Not killing Claudius in the church, he rashly and mistakenly kills Polonius, assuming incorrectly that Claudius quickly ran up to Gertrude’s room. The stakes are raised for Claudius and Hamlet. Polonius’s death missing body incense Claudius who is overwrought with fear knowing his enemy Hamlet has put a target on his back.
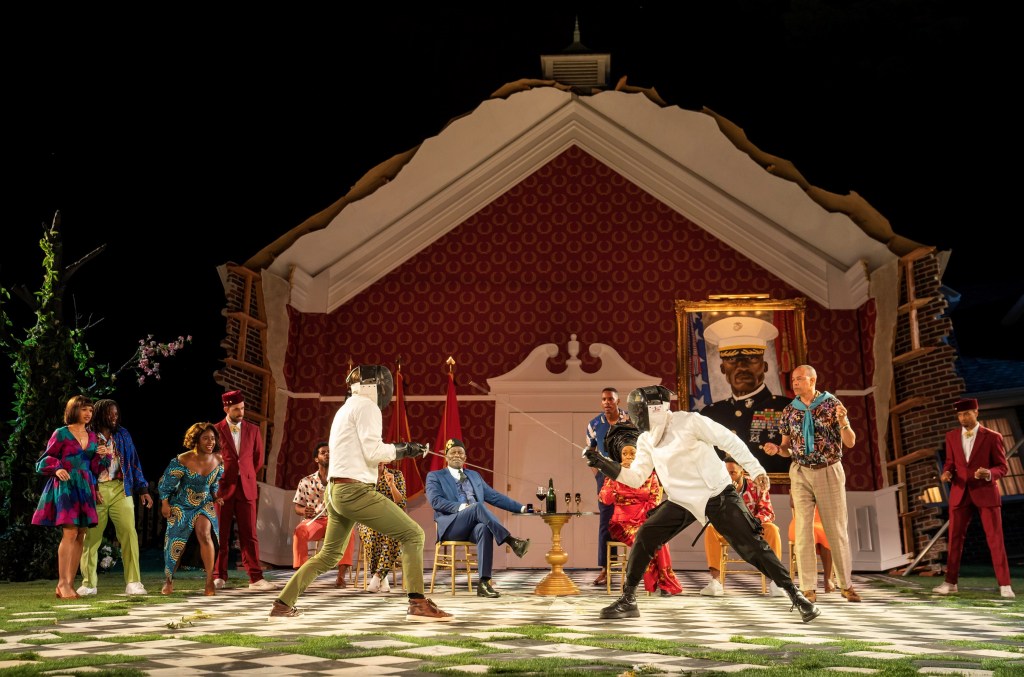

Once more, the “time is out of joint,” and Hamlet defers vengeance and subjects himself to Claudius, finally revealing where Polonius’ body is. For Gertrude’s sake, Claudius sends Hamlet away with the orders for others to kill him in a plan that fatefully backfires.
Leon’s version has clarified the stakes for Claudius to escape accountability, manipulating Laertes (Nick Rehberger) from killing him by blaming Hamlet. Thompson conveys each of these cover-ups with precision. Also, clarified is Blankson-Wood’s angst and struggle confronting his father’s murderer. His use of irony as a weapon to prick Claudius’ conscience is superbly rendered as are his soliloquies whose philosophical constructs tie him in emotional knots. Hamlet, knowing that he is stuck in a morass with no way out, recognizes that like the other characters, he is on a collision course with destiny and ruination which is foreshadowed at the beginning with Boritt’s set.
Also, clarified in this version is Toussaint’s Gertrude who is in a state of ambivalence and guilt stirred by Hamlet’s antic behavior, which she suspects is his response to her marrying Claudius. When their confrontation occurs after Hamlet kills Polonius, she knows her relationship with Claudius must be thrown over, yet she hesitates and discusses Hamlet with Claudius ignoring Hamlet’s wise counsel. The doom she recognizes in Ophelia’s madness will only bring more sorrows, a trend which both Claudius and Gertrude comment upon. Toussaint’s description of Ophelia’s drowning is heartfelt and mournful.
The flow of events coheres because the through-line of Claudius and Gertrude in conflict with Hamlet is maintained with intensity. Stripping Norway from the action and leaving Fortinbras out of the conclusion is to the purpose of Leon’s emphasis of the familial tragedy. The contrast of the good son and man of action who achieves justice (Fortinbras) with Hamlet’s flawed son of inaction who is Fortune’s fool, exacerbating destruction via revenge gone wrong would have pleased Queen Elizabeth I. Contrasting the two Prince’s and showing the heroic one in Fortinbras is an encouragement of how royalty should rule. However, it doesn’t fit with the themes that Leon emphasizes, especially that a “house divided against itself cannot stand.”
Hamlet concludes with the slaughter of two families tainted by their association with a corrupted king, out from which there is no release except death. A final theme current for our time suggests that unless individuals stand against usurpers of power, the usurper and all who are his accomplices by not bringing him to justice will pay the forfeit of their lives and fortunes.
However, only Miller’s Horatio understands the full story of Hamlet and the striving between vengeance and justice. That vengeance brings disaster is why the ensemble finishes with the actors’ song that they sang when Hamlet first meets them. It is poignant and true and heartfelt when the spirit of Ophelia joins them and together they sing, “I could tell you a tale, God’s cry. It could make the God’s cry.”
Kudos to the ensemble and the creative team who carry Leon’s vision of Hamlet into triumph. These include those not already mentioned: Jessica Jahn’s colorful costume design, Earon Chew Nealey’s hair, wig and makeup design, Camille A. Brown’s choreography and Gabriel Bennett for Charcoalblue and Arielle Edwards for Delacorte’s sound system design.
For tickets to this unique Hamlet which has one intermission, go to their website https://publictheater.org/productions/season/2223/fsitp/hamlet/
‘Slave Play’ by Jeremy O. Harris, An Explosive, Archetypal Look at Power, Sadomasochism and Oppression Through the Mythic Lens of “Black” and “White”

(L to R): Ato Blankson-Wood, Chalia La Tour, Joaquina Kalukango (kneeling), Irene Sofia Lucio, Sullivan Jones, Annie McNamara, Paul Alexander Nolan, and James Cusati-Moyer. in ‘Slave Play’ by Jeremy O. Harris, directed by Robert O’Hara (Matthew Murphy)
Slave Play by Jeremy O. Harris is a mind-bending, brain-slamming earthquake which will strike your soul and disturb you emotionally. Despite your desire to remain unaffected, you will react. Good live productions stir us. The finest plays rock us off our complacency and shatter our intellectual stasis. Slave Play, directed by Robert O’Hara, currently at the Golden Theatre, does that and more. Memorable and profound, it is the epitome of its sardonic genre. And in its ancient modernism, it rises to a level that melds tragedy and comedy.
The searing truths that run through Harris’ themes confound to a new clarity, especially if you see yourself as color blind and gender blind. Harris gouges out our assumptions and parades them in front of our unwillingness to perceive our hidden feelings about race, sex and power, teasing us in the process. By gaming his audience, Harris is all about stopping the games and taking off the masks. And he achieves this through the gyrations of his characters, three mixed-race couples who have sought therapy for their anhedonism (inability to feel pleasure-a symptom of depression and other ailments) with their partners.
The three couples sign up for “Antebelleum Sexual Performance Therapy” in order to expurgate their conflicts concerning race and sex that are ancient unconscious impulses or lesions borne from centuries of oppression in America from before the Civil War. It is an oppression that is in “black” and “white” unconsciousness that transcends skin color because the current society has historical remnants of the degradation of the “peculiar institution” which deformed the psyches of both masters and their slaves, the oppressors and the oppressed. Each couple suffers from these hidden twisted notions that they have ingested from living in American society. It has impacted them and they want a release from their suffering which manifests as alienation from their long-term partners.
This is a spoiler alert!

Joaquina Kalukango, Paul Alexander Nolan in ‘Slave Play,’ by Jeremy O. Harris, directed by Robert O’Hara (Matthew Murphy)
Only, you don’t know that at first. Indeed, initially as the play opens, we believe we are watching a scene from the antebellum South involving the abuses of the master slave relationships via sexual sadomasochism. With these scenes highlighting the sexual “play” of the marriage partners, Harris hits us between the eyes and in the core of our presumptions in the hope of laying bare the psycho-sexual racial myths that lurk in our souls.
Thus, everpresent in the scenic design by Clint Ramos is the plantation mentality: the desire to oppress and degrade employing the vehicles of sex. Using mirrors Ramos reflects the white southern archetype of the white antebellum plantation of Master MacGregor’s mansion that encircles the proscenium. Throughout most of the production, the projection of the white plantation remains in the background, symbolizing that we may think we have been released from our history, but it resides just below the surface of consciousness in our relationships and especially in our relationships with members of another race concerning issues of true intimacy and honesty.
It is in this plantation setting that the characters dig in to expose their sadomasochistic impulses from a racist past that they have unconsciously internalized and must expiate to heal their marriage relationships. Harris humorously twits the audience’s assumptions about black sexual prowess and sensuality in the opening scene with each mixed race couple as they play out their fantasies to free themselves of the bondages that hamper reaching a satisfying closeness with their partners.
Gary (Ato Blankson-Wood) and Dustin (James Cusati-Moyer) portray the gay couple who cannot please each other. They engage in the fantasy of master/slave verbal abuse donning fictional characters, Dustin as an indentured servant and Gary as a slave who has been put in charge of him. Through the play acting, Gary reaches fulfillment but in his response to this, he upsets Dustin. There is only a partial breakthrough, tenuous at best. They have not exorcised the notions that harm them.
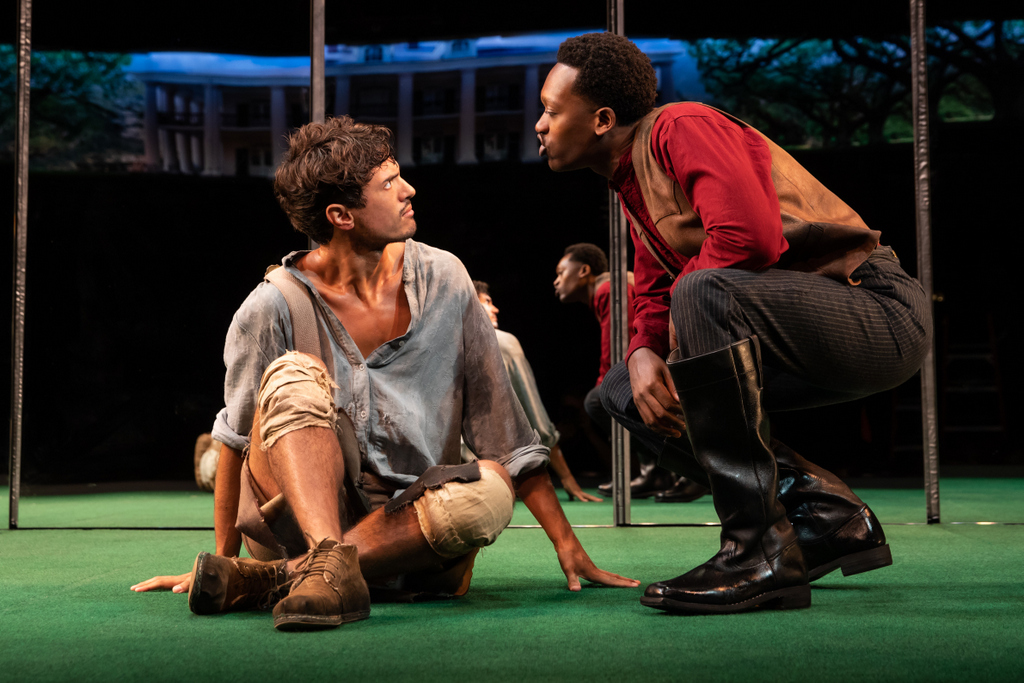

(L to R): James Cusati-Moyer and Ato Blankson-Wood in ‘Slave Play,’ written by Jeremy O. Harris, directed by Robert O’Hara (photo by Matthew Murphy)
Phillip (Sullivan Jones) and Alana (Annie McNamara) portray a married couple who cannot achieve a hot intimacy until they enact their antebellum sex play. In their fantasy Alana is Master MacGregor’s wife and Phillip is her house slave who does what she wants. What pleases her is to take over the masculine role while he takes on the feminine role during a sexual encounter, something which makes her freer for intimacy with her partner. However, they too have issues because of Phillip’s race identity problems which he is loathe to admit and which to him are invisible.
The couple Kaneisha (Joaquina Kalukango) and Jim (Paul Alexander Nolan do not progress on this fourth day of the sexual fantastic. Jim finds the therapy ridiculous and demeaning. Ironically, it is Kaneisha who has engineered the roles and takes the lead in their improvisation. She portrays the slave and Jim (who has a British colonial accent-another irony) is the overseer who commands her unjustly, then sexually uses her as she uses him. But Jim finds her fantasy an impossibility and will not subject himself to it. Is this not a case of subliminal control and domination over his wife Kaneisha?
With each of the couples’ fantasies, there are strong elements of sadomasochism which are supposedly exorcised in the service of removing blocking psychic layers that impede the couples’ pleasure with each other. Unfortunately, Jim has stopped the process for all the couples. A condition of the therapy they have all agreed to is that if one cannot continue, all must not continue. When the couples meet to discuss and analyze what they felt during their fantastic sexual exploits exposing their sub rosa “plantation” mentality, the conflict is on. And Harris’s characterizations continue on a profound and humorous track as problems arise. Each couple ends up confronting their partner with results that are both humorous and poignant.
At this juncture social scientists and therapy guides Patricia (Irene Sofia Lucio) and Tea (Chalia La Tour) attempt to analyze and reaffirm their subjects’ positive changes as a result of the antebellum sexual play therapy. That the researchers do this in a controlled, manipulative way is an irony considering that all seek freedom from their internalized racial oppressions (the predator/prey elements of human behavior). Harris sardonically reveals these individuals, including the scientists, may be duping themselves into believing they’re getting closer to a “clear,” when what they seek cannot be achieved in a week-long process, regardless of how extreme the interventions. Perhaps, what has been internalized must be overthrown with individual introspection on the part of both partners after a long period of time. There is no quick fix except sustained love, growth, patience, understanding and the will to be close which eventually, through loving practice, will manifest. Maybe.
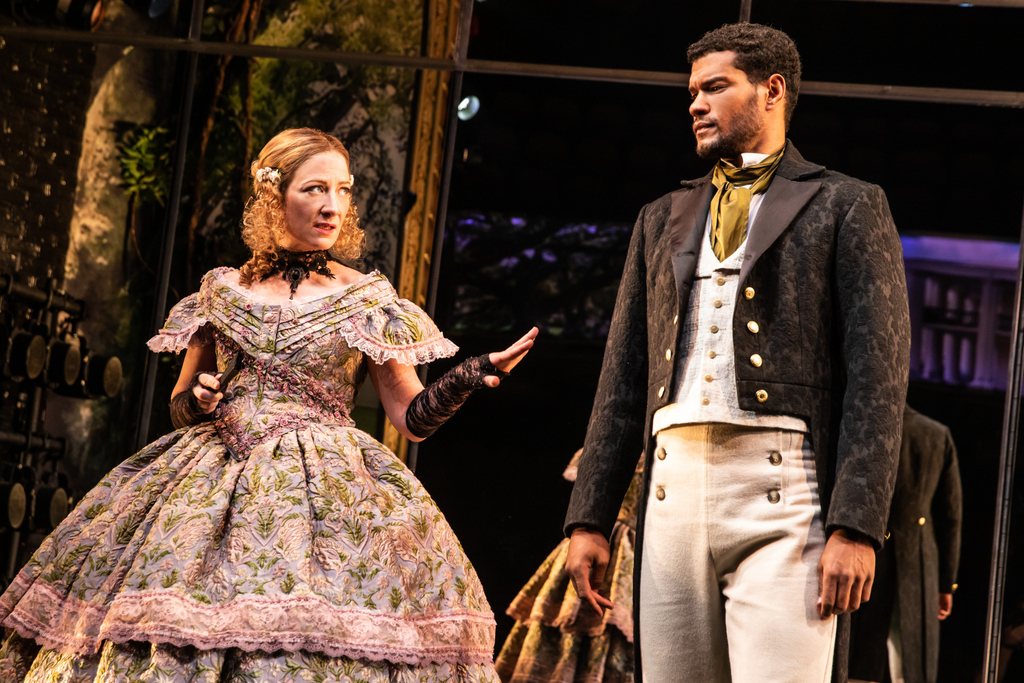
Annie McNamara and Sullivan Jones in ‘Slave Play,’ written by Jeremy O. Harris, directed by Robert O’Hara (Matthew Murphy)
The “liberal” posture which infects the “white” characters who are coupled up with their “darker” equally infected counterparts Harris explodes by the play’s end, as he disintegrates the notion that racism’s complexities may be dealt with through extreme interventions and quickie therapies. Especially for couple Kaneisha and Jim there has been a break through in their relationship at great cost to Jim who upon facing himself, dislikes what he perceives himself to be. Whether they continue together after this turning point doesn’t matter. Each have understood a soul revelation and will never be the same again.
Harris’ Slave Play instructs us about our perceptions, our attitudes and our willingness to go to that place that is uncomfortable to shed the pretense and stop pandering to faux racial equanimity and justice. That is why the curtain mirror that reflects the audience’s faces effected by Clint Ramos’s superb scenic design is a clever touch in keeping with Harris’ themes. The more visible reflections are for the audience members who are down front in the expensive seats.
Shouldn’t we examine our own proclivities and assumptions about sex, race and power dynamics? Or should we just ignore that there is a confluence of currents roiling in the subterranean waters of our souls about race? How do we overthrow our past and live freely without internalized cultural oppressions: misogyny, paternalism, institutional racism, body objectification, appearance fascism, sexism, chauvinism, reverse racism and impulses of white supremacy which move along a continuum from faint to furious? All of these oppressions impact our intimacy with ourselves and others, whether we are in mixed race relationships or not. Harris suggest we investigate these tantalizing questions which are not for the faint of heart.
As Americans steeped in a social history of racial power dynamics that continue today, though many are loathe to admit it, one cannot view this play as a light observer. To have the themes resonate, one should follow the characters to the most profound levels and then consider the myths, the conceptualizations about being black, white and gradations of both culturally. One must see with new eyes what has not been seen before at this crucial time when leaders speak to and embrace racist hate groups (KKK, Neo Nazis, etc.) curry favor with the likes of David Duke and Richard Spencer, and give political advisors like Steven Miller great power and moment over US Immigration policy with the precise intent to discriminate, promote fear and abuse for political purposes.
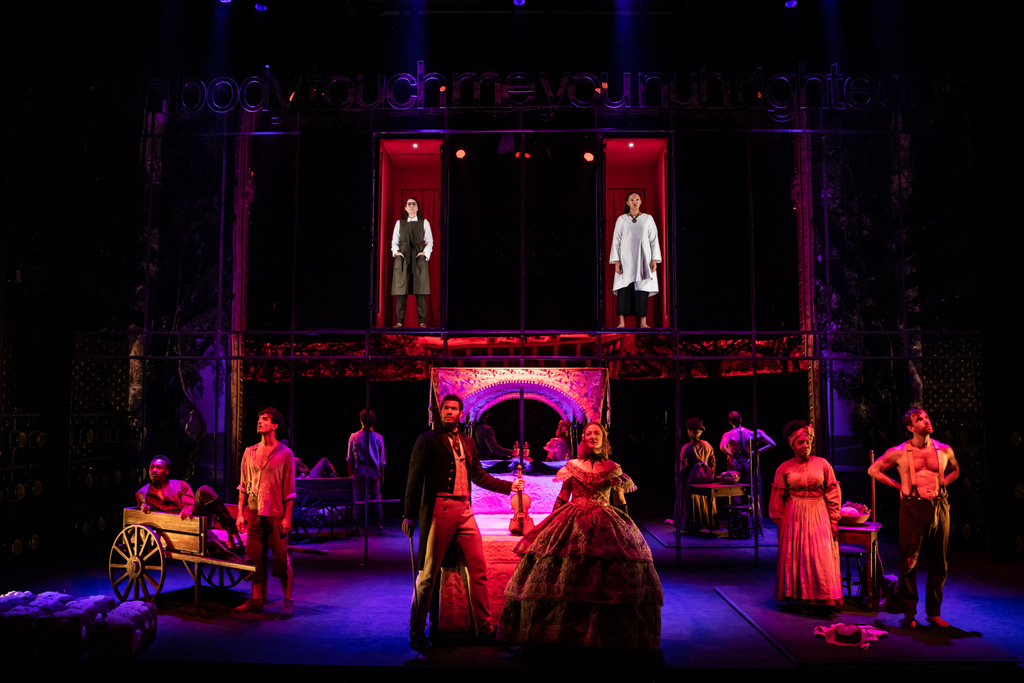

(On Ground L to R): Ato Blankson-Wood, James Cusati-Moyer, Sullivan Jones, Annie McNamara, Joaquina Kalukango, Paul Alexander Nolan. (In red boxes L to R): Irene Sofia Lucio and Chalia La Tour, ‘Slave Play,’ directed by Robert O’Hara, written by Jeremy O. Harris (Matthew Murphy)
Harris intends to shock us into a dialogue to confront our own assumptions on whatever level we can, so we might grow as Americans who recognize their rich yet horrific social, political and cultural history. As Harris’ characters recognize they are stymied and self-harmed by their own misconceptions, depressions and failures to deal with the historical, ancestral folkways and noxious human behaviors they’ve internalized, at least they attempt to overthrow them. Shouldn’t we, Harris suggests? But are we up for this? We should be! Look at the gun shootings at synagogues and black churches.
Until there are conversations about such controversial topics as Slave Play raises, the country’s divisiveness may be exploited by pernicious leaders and malevolent foreign intelligence services who foment racial hatreds to satisfy their own personal agendas. Our culture’s current divides are toxic. To mitigate them requires a complexity of understanding and introspection on a personal level. Harris indicates dealing with this on an interracial, mixed couple level may be the way to get there if there is love, patience, understanding and will. The issues are hyper complex and are not adequately answered by quick fixes and exotic hyperbolic interventions which themselves represent the internalized predator/prey, oppressor/oppressed remnants of racism.
The ensemble is wonderful and acts seamlessly together with a comfortability at behaviors which appear impossibly raw. The therapy session is particularly acute, funny, authentic and smashing. All the actors are standouts as is required with such an amazing play. Kudos to the director who shepherded them. Each couple ends up confronting their partner with results that are both humorous and poignant.
The design team also shines: Dede Ayite (costume design) Jiyoun Chang (lighting design) Lindsay Jones (sound design & original music) Cookie Jordan (hair & wig design). Conceived at New York Theatre Workshop where it ran in from November 2018 to January 2019, Slave Play has come to Broadway where it is provoking consternation, confusion and revelation. It runs with no intermission until 19 January. There are too many reasons why you should see this play if you are an American, and especially if you have a bit of residual racism within and are adult enough to laugh at yourself. For tickets and times CLICK HERE.









